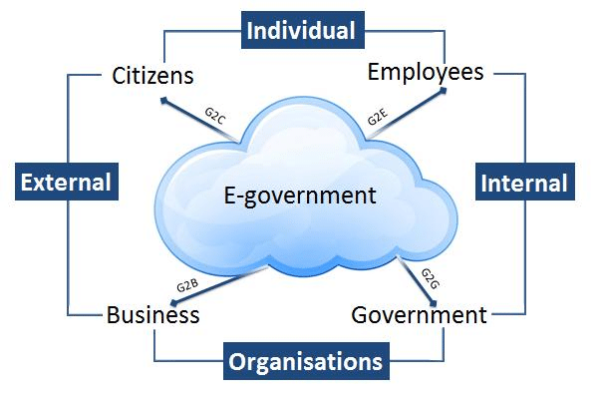
In recent years, Africa has experienced a remarkable digital transformation, with governments leveraging Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to enhance service delivery, foster economic growth, and empower citizens and businesses alike. Through innovative Government-to-Citizen (G2C) and Government-to-Business (G2B) ICT projects, African nations are overcoming traditional barriers and embracing the opportunities of the digital age. This article explores the key initiatives and the profound impact they are having across the continent.
Government-to-Citizen (G2C) ICT Projects:
- E-Government Portals: Many African governments have developed centralized e-government portals, providing citizens with convenient access to a wide range of public services and information. These portals enable users to apply for documents such as passports and driver’s licenses, pay taxes and bills online, and access important government announcements and resources. By streamlining administrative processes and reducing bureaucratic red tape, e-government portals enhance efficiency and transparency while improving citizen satisfaction.
- Digital Identity Systems: The implementation of digital identity systems is revolutionizing service delivery in Africa. By issuing unique identification numbers and digital IDs to citizens, governments are simplifying access to essential services such as healthcare, education, and social welfare. Digital identity systems not only facilitate more efficient and targeted service delivery but also help combat fraud and corruption, ensuring that resources reach those who need them most.
- Mobile-Based Services: Mobile technology has emerged as a powerful tool for delivering government services directly to citizens, particularly in remote and underserved areas. Mobile-based applications and SMS platforms enable citizens to access vital information, receive alerts and notifications, and even participate in governance processes such as voting and public consultations. By leveraging the widespread availability of mobile phones, governments are bridging the digital divide and ensuring that all citizens can benefit from the opportunities of the digital age.
Government-to-Business (G2B) ICT Projects:
- E-Procurement Systems: E-procurement systems are transforming the way businesses interact with government entities, streamlining procurement processes, and enhancing transparency and accountability. By digitizing procurement workflows and implementing online bidding platforms, governments are reducing costs, minimizing delays, and improving competition among suppliers. E-procurement systems also enable small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to compete on a level playing field, driving economic growth and fostering entrepreneurship.
- Online Business Registration: Simplifying the process of starting and operating a business is critical for promoting entrepreneurship and economic development. Many African governments have implemented online business registration systems, allowing entrepreneurs to register their businesses quickly and efficiently from anywhere with an internet connection. By eliminating cumbersome paperwork and bureaucratic hurdles, online business registration systems encourage formalization, stimulate investment, and create a more conducive environment for business growth.
- Digital Trade Platforms: Facilitating cross-border trade is essential for unlocking Africa’s economic potential and accelerating regional integration. Digital trade platforms enable businesses to connect with trading partners, access market information, and complete customs clearance procedures online. By reducing trade barriers and transaction costs, digital trade platforms promote trade facilitation, expand market access, and drive economic diversification and integration across the continent.
Impact and Challenges:
While Government-to-Citizen and Government-to-Business ICT projects hold tremendous promise for Africa’s development, they also face several challenges. These include limited internet connectivity and digital literacy, inadequate infrastructure, cybersecurity risks, and regulatory barriers. Addressing these challenges requires strong political will, strategic investment in ICT infrastructure, capacity building, and effective public-private partnerships.
In conclusion, Government-to-Citizen and Government-to-Business ICT projects are playing a transformative role in Africa’s development journey, unlocking new opportunities for citizens and businesses and driving inclusive growth and prosperity. By harnessing the power of technology and innovation, African governments can continue to accelerate progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals and building a brighter future for all.